Safety glass
Reduce the risk of glass breakage and related injuries

Safety glass refers to glass with additional safety features that make it less likely to pose a threat to the general public when broken. There are two types of safety glass: tempered glass and laminated glass tested in conformance with applicable standards are considered as safety glass.
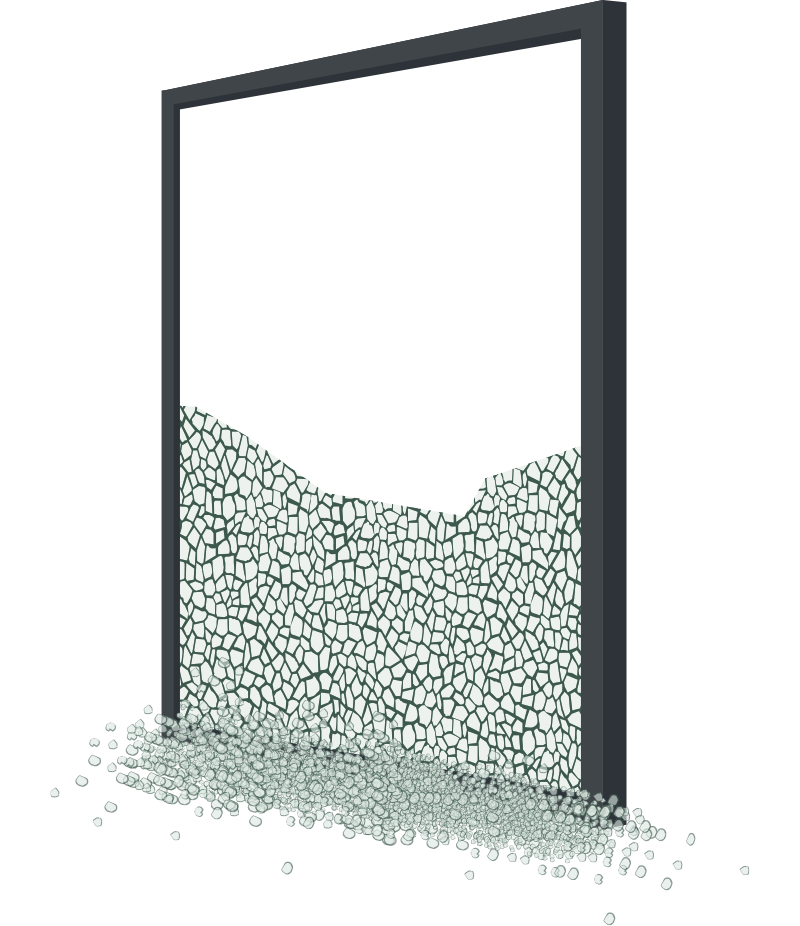

Safety with tempered glass
Tempered glass breaks into small pieces which reduces the potential injury from cutting or piercing a person impacting the glass. It is important to bear in mind that fragments of tempered glass tend to fall out of the frames once broken, creating a hole or opening in the building envelope that allows occupants to fall through the opening.

Safety with laminated glass
In contrast to safety features provided by tempered glass, fragments of laminated glass typically stay adhered to the interlayer and remain in the frames. This breakage characteristic of laminated glass contributes to human safety by protecting occupants from falling through the opening to the lower level and providing protection from dangerous flying or falling glass fragments.
The different breakage pattern between tempered glass and laminated glass plays an important role during glass selection for human safety protection.
You need to add solar control and/or thermal properties to the glazing? Guardian SunGuard™ solar control glass products for architectural applications can be tempered or laminated.
What are the applications where safety glass is required?

Human impact resistance
Safety glass is typically required in hazardous locations with a high risk of accidents from human impact. Typical applications are:
- Large windows near walkways
- Glass doors
- Storefront windows
- Ground Level glazing
- Glass facades
Shard fallout and fall-through protection
Overhead glazing such as skylights and sloped glazing located above walking areas should consist exclusively of laminated safety glass, with a minimum of 0.76 mm PVB for the lower pane. Design load requirements may even demand higher standards.
Some examples of glazing that may require more stringent standards include:
- Walk on glazing
- Roof and horizontal glazing
- Barrier glazing
- Stairs and ramps
- Canopies
- Balustrade


Debris Impact resistance
In addition to accidental impact, safety glass is recommended to minimize damage from natural causes. For example, violent windstorms such as hurricanes or tornados can cause damage to glazed openings from airborne debris impacts. For projects located in high wind areas, local building codes have specific requirements for impact resistance for both glass and framing systems.
👉 Expert talk
“Understanding the final application and the combination of all the requirements is important when selecting which safety glazing option is the most appropriate. Although the type of glass chosen will vary depending on local building code standards and the specific requirements of the project, there are a number of potential options and combinations to consider with both tempered and laminated safety glass. Guardian Glass team of experts can recommend what safety glass is the most suited to your project through static calculations (glass thickness, tempered or laminated glass) and based on local regulations.”
What test should glass pass to be classified as safety glass?
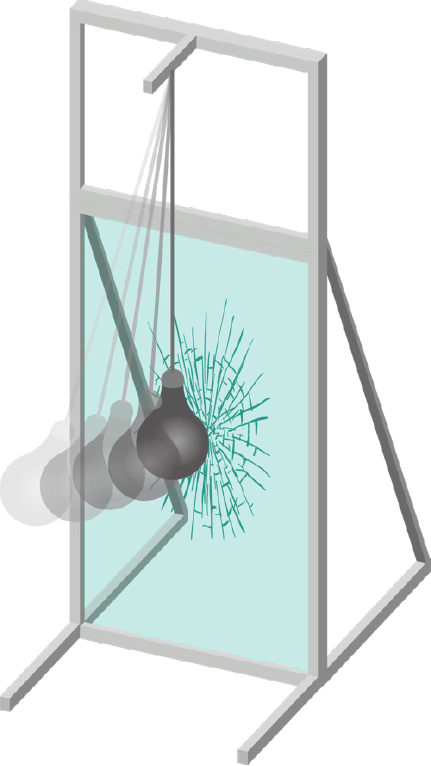
Human impact safety – the pendulum test
Local building codes and regulations worldwide specify test methods for safety glass used for human impact safety protection. While these standards have some differences, they have similar test procedures to assess safety glass performance.
For safety glass, the codes stipulate a pendulum test to simulate glass subjected to human impact force. In general, the test involves impacting the glass sample with a specific weight that is dropped from a specific height. European standards use standard twin-tires while North American standards use a weighted bag to simulate a human body.
Debris Impact resistance
- Debris impact resistance performance applies to the overall glazing system. The test procedure involves subjecting the glazing system to a specific impact force from large and small objects that can fly and hit the glass during extreme wind conditions.
- Laminated glass is commonly used for debris impact resistance. Glass thickness and interlayer type of the laminate construction is dictated by the wind speed and the level of impact protection required for a specific project.
While both tempered glass and laminated glass are considered safety glass, the decision whether to use tempered glass or laminated glass is dictated by local building code requirements and safety criteria applicable for a specific project.

Want to know more about safety glass?
For more details on what results laminated and tempered glass should achieve at the pendulum test to be qualified as safety glass, view our training module on Safety and Security.

Safety glass Standard and Conformance
In the US, currently, safety glass is described in CPSC 16 CFR 1201 and/or ANSI Z97.1.
In Europe, currently the standard describing safety glass is EN 12600 – called, Pendulum test- Impact test method and classification for glass, to simulate the impact of a human body.
Other regions of the world may have different standards for safety glass.
In addition, North America has specific standards for debris impact resistance, which are ASTM E1886 and ASTM E1996.
What is the difference between safety and security glazing?
Safety is defined as the condition of being protected from injury or loss due to accidents or natural causes. Some regions refer to this condition as passive safety.
Security is defined as the condition of being protected from injury or loss due to deliberate or intentional actions including burglary/forced entry, ballistics, and bomb-blast. Some regions refer to this condition as active safety.
See our safety glass products
Need to compare the performance of our products? Visit our product section to search, compare and filter through our wide range of glass solutions.
-

Guardian LamiGlass® ExtraClear
Guardian LamiGlass® is a laminated glass made of two or more panes bonded together with clear PVB interlayers. By using different glass types, and varying the number of interlayers, it can deliver a wide range of performance benefits.
See more -

Guardian LamiGlass® UltraClear®
Guardian UltraClear® LamiGlass™ Neutral glass, with Saflex® Crystal Clear PVB, is unlike any other laminated, low-iron safety glass. With exceptional neutrality and transparency, it has an aesthetic appeal very close to monolithic Guardian UltraClear – regardless of the viewing angle.
See more -

Guardian LamiGlass® Acoustic
Guardian LamiGlass® Acoustic is a laminated glass with an advanced interlayer that delivers significantly improved sound insulation compared to standard laminated glass.
See more -

Guardian LamiGlass® Color
Guardian LamiGlass® Color is a laminated glass that features a colored PVB interlayer. This means that not only does it help protect and secure it brings an enhanced aesthetic appeal to every project.
See more -

Guardian Bird1st™
Guardian Bird1st™ helps to prevent birds from colliding with buildings – by featuring striking and highly visible patterns to birds, while remaining discreet to humans.
See more
Whether you're drawing skyscrapers, remodeling homes or designing a new project, our team of glass experts is ready to help you find the right glass for your project.
